Linking Pages
Hyperlinks
The original purpose of the World Wide Web was to provide a
mechanism for non-linear access to information. In order to activate this type of retrieval,
information is packaged as a set of Web pages, and then hypertext links, or
hyperlinks are created to navigate from one page to another in whatever sequence the reader
prefers. In a later tutorial, the varieties of page links are discussed more fully. Here
you are introduced to the basic concept of linking and shown how to set up text links for
navigation between pages.
Most often a link from one page to another is made by creating a
text "hot spot" on one page that, when clicked with the mouse, opens a second page which
replaces the first page in the browser window. The string of text that is made sensitive to
a mouse click can be a single word or several words, usually suggestive of the contents of
the destination page. Normally, a second link appears on the linked page for return to the
original page. It is considered poor Web citizenship to leave visitors at the end of a
series of links with no way to get back to the starting page.
In the illustration in Figure 2-26 two text links cause navigation
to different pages. On the linked pages a text link provides for return to the original
page.
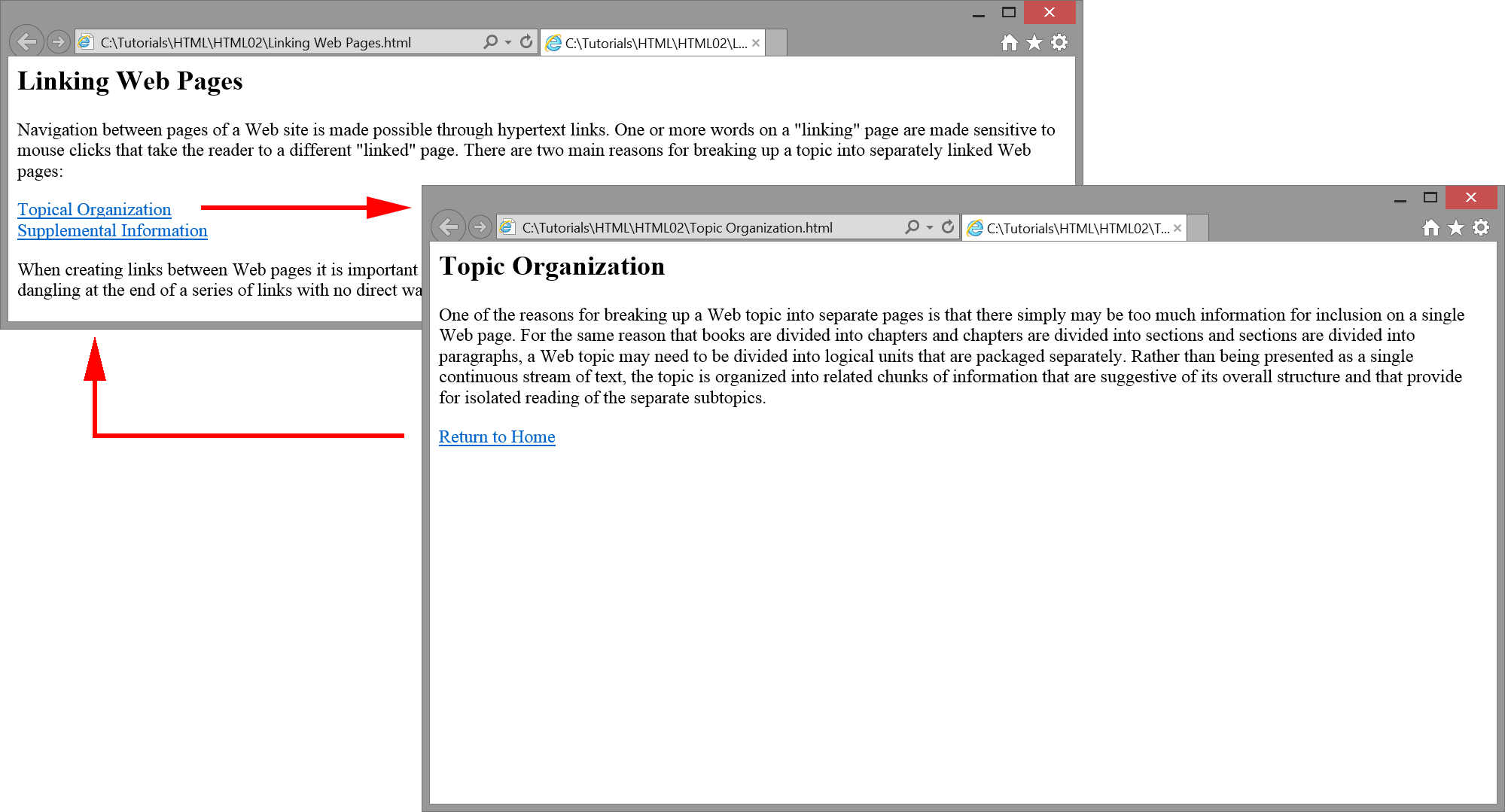 Figure 2-26. Text links between pages.
Figure 2-26. Text links between pages.
You can test these links by clicking the "Linking Web Pages" text
link below. The original page is opened in a separate browser window. From there, you can link to
and return from two different pages.
The <a> Tag
The most common type of link is a clickable word or phrase that
transfers directly to the target page. A text link of this sort is created by surrounding the
text string with an <a> tag (also called an anchor
tag), and specifying the location of the page to which to link. The <a>
tag is classified as a container and inline-level tag. The basic format for coding this tag is shown in
Figure 2-27.
<a href="url">linking text</a>
Figure 2-27. General format for <a> tag.
The href (hypertext reference)
attribute specifies the URL of the linked page.
Links can be made to other pages at the local Web site or to pages
at remote sites anywhere on the World Wide Web.
If the linked page is in the same location ‒ in the same directory
‒ as the linking page, then the URL is simply the page name. This local link is called a
relative link since the path to the linked page is relative to the location of the
linking page.
When linking to a remote site, the URL must be a full Web reference
including the "http://" protocol followed by the domain
name of the site. This external link is called an absolute link since the path to
the linked page is a full Web address.
The <a> tag surrounds a string of text that is to be made
click-sensitive and that activates the link. Usually the text is
descriptive of the destination link. It can be a single letter, a word, a phrase, or any amount of
text that can reasonably serve as a link. When this text is clicked, the linking page is
immediately replaced by the linked page in the browser window.
The <a> tag is an in-line tag. It does not add any new lines or spaces
before or after the content which it wraps.
Local Links
When creating your own Web site, most of the links will be between
your own pages. The easiest way to store these pages for linking is to save them in the
same location. That is, in the same disk directory or on the same diskette or storage unit.
In this case the URL specified in the <a> tag is simply
the name of the page.
In the example in Figure 2-26 there are three Web pages named Home.htm,
Organize.htm, and Supplement.htm.
The Home.htm page contains text links to the other two pages and is coded as follows.
<h2>Linking Web Pages</h2>
<p>
Navigation between pages of a Web site is made possible through hypertext
links. One or more words on a "linking" page are made sensitive to mouse
clicks that take the reader to a different "linked" page. There are two main
reasons for breaking up a topic into separately linked Web pages:
</p>
<p>
<a href="Organize.htm">Topical Organization</a><br>
<a href="Supplement.htm">Supplemental Information</a>
</p>
<p>
When creating links between Web pages it is important to provide return
links to the linking pages. The page author should not leave readers dangling
at the end of a series of links with no direct way to return to the home page.
</p>
Listing 2-16. Code for linking pages.
Notice the line containing the code
<a href="Organize.htm">Topical Organization</a>
An <a> tag surrounds the string of
text "Topical Organization" to convert it into a hyperlink to open the Organize.htm
page in the browser window. Only the name of this page is required as the href
URL since the linked page appears in the same directory as the
Home.htm page from which the link is made. Similar coding links to the
Supplement.htm page. When either of the two links is clicked, the
associated page is retrieved and loaded into the browser, replacing the Home.htm page.
When either Organize.htm or Supplement.htm
are showing in the browser window, it is easy to return to the Home.htm
page by clicking the Back button on the browser's Tool Bar. However,
it is a better navigation
solution to code your own internal links between pages. In other words,
both the Organize.htm and Supplement.htm pages should
include, as shown here, their own links back to Home.htm.
Coding for the Organize.htm page is shown
below. Here the string
of text "Return to Home" is made into a link by surrounding it with
an <a> anchor tag. A click on this
link reopens the Home.htm
page in the browser window. Similar coding appears on the
Supplement.htm
page to return to the home page.
<h2>Topic Organization</h2>
<p>
One of the reasons for breaking up a Web topic into separate pages is
that there simply may be too much information for inclusion on a single Web
page. For the same reason that books are divided into chapters and chapters
are divided into sections and sections are divided into paragraphs, a Web
topic may need to be divided into logical units that are packaged separately.
Rather than being presented as a single continuous stream of text, the topic
is organized into related chunks of information that are suggestive of its
overall structure and that provide for isolated reading of the separate
subtopics.
</p>
<p><a href="Home.htm">Return to Home</a></p>
Listing 2-17. Code for linking back to original page.
The manner in which you set up links between your pages is at your
discretion. To a large extent, it depends on how you subdivide your site into separate pages
and the way in which the separate topics relate to one another. Make sure there are
no "dead end" pages where visitors arrive with no way to get back to where they came
from.
Remote Links
If you know the URL of a Web site anywhere on the World Wide Web
you can make a link to that site. This URL is normally in the form
http://domain name
where the http protocol prefixes the site
location (domain name).
This type of absolute reference takes you to the home page of that
site. The following link code,
for example, is used to open the home page at www.google.com.
<a href="http://www.google.com">Go to Google</a>
Go to Google
Figure 2-28. Code and link to an external Web site.
To find out the URL of a Web site simply go there and read the URL
that appears in the Address box of your browser. Copy this address into the
href attribute of your <a> tag and add the text to
make a clickable link.
If you are linking to a particular page at a remote site then the
domain name is followed by a path through the directory structure to the specified page. For
instance, the following URL accesses a page at sports.yahoo.com containing links
to various business sites and services.
<a href="http://sports.yahoo.com/nfl/teams/">NFL Teams</a>
NFL Teams
Figure 2-29. Code and link to an external Web site and directory structure.
This page is located in the teams subdirectory of the nfl directory of the
site. The URL is taken from the browser's Address box for the displayed page.
Link Colors
Depending on your browser's settings, a text link shows up in
different colors as a visual clue to the status of the link. Before a linked page is
visited for the first time its text link displays in blue. After the page is visited, the link
changes to purple. You can tell at a glance whether or not you have previously visited
a page.
In a later tutorial you will learn how you can change these default
colors for links that you code.
The target Attribute
By default, linked pages are opened in the same browser window as
the linking page subsequently replacing it.
When linking to a remote site, a risk is that your visitors will
navigate the remote site and eventually lose contact with your site. They can repeatedly click the
browser's Back button to get back to your site, but if they have wandered around the remote site to any great
extent then backing up to your site may be impractical. You end up losing your visitors to the remote
site.
One way around this problem is to always link to remote
sites in a separate browser window. It is quite easy to open a page in a different window. Simply add the
attribute target="_blank" to your <a> tag
as shown below for the above link to the Google site.
<a href="http://www.google.com" target="_blank">Go to Google</a>
With this technique, visitors can browse the remote site as much as
they wish in a second browser window, and by closing that window return immediately to
your linking page in the original window.
Creating text links as described here represent only a couple of
the ways in which hyperlinks can tie together multiple Web pages. In a later tutorial, other
varieties of links and linking methods are discussed.